Hello Nature readers, would you like to get this Briefing in your inbox free every day? Sign up here.
The Utah FORGE project has reduced the cost of drilling boreholes for enhanced geothermal systems. Credit: Dr. Clay Jones
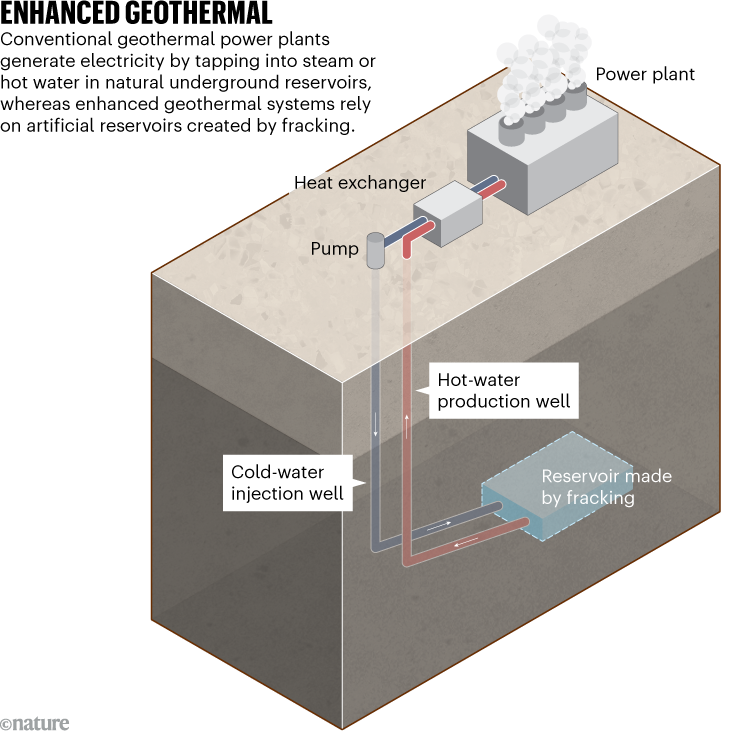
Investments in geothermal heating up
As tech giants Microsoft, Google and Amazon strike nuclear-energy deals, companies including Meta are investing in a different source of low-carbon energy — enhanced geothermal systems. The approach involves creating hot springs by drilling several kilometres deep and injecting water and sand at high pressures. Most previous attempts have failed to extract notable amounts of energy, but recent advancements in technologies used in the oil and gas industry have helped researchers improve the technique.
Drug resistance seen in severely ill kids
Resistance to key malaria drug artemisinin has been detected for the first time among children in Africa with severe disease. A study of children in Uganda showed that around 10% of those with severe disease showed partial resistance to artemisinin, meaning the drug took longer than five hours to kill half of the malaria parasites. “If this is verified by other studies, it could change guidelines for treatment of severe malaria in African children, and they are the biggest target group by far,” says Chandy John, a specialist in paediatric infectious diseases.
Trust in US scientists (slightly) recovering
Trust in scientists has increased in the United States for the first time since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, but only slightly. The results of a survey conducted two weeks before the US presidential election found that the proportion of those polled who believe that scientists act in the best interests of the public rose from 73% a year ago to 76% now. Although it’s a step in the right direction, the number is still lower than the 87% who trusted scientists in April 2020.
Reference: Pew Research Center report
Features & opinion
Some academics flee Twitter for Bluesky
Is #ScienceTwitter becoming #ScienceSky? A wave of academics and researchers say they have defected from the social media platform X. “It has become a toxic cesspool, is owned by someone I despise, and has become a tool for disinformation,” wrote former university president Paul LeBlanc. Many are heading to upstart Twitter-lookalike Bluesky, which has reported an explosion in users in recent days. Others worry that turning away from Twitter is tantamount to a retreat from public engagement. “I think it is bad for the commons if all the academics disappear and only talk to each other,” says economist Paul Novosad.
Inside Higher Ed | 6 min read (free reg required)
Futures: Thixotropic world
Time and space become fluid under stress in the latest short story for Nature’s Futures series.
Five best science books this week
Andrew Robinson’s pick of the top five science books to read this week includes the story of how Chinese-language computers adapted to using QWERTY keyboards and delves into the brain science of obedience in an exploration of atrocities committed while ‘just following orders’.
Podcast: How skull bone marrow thwarts ageing
Unlike in most other bones, the bone marrow in the skull seems to expand with age, gaining volume and blood vessels. “We think that this is, in a way, trying to compensate for the other failing bone-marrow compartments,” says cranial-vascular biologist and study co-author Bong Ihn Koh. And in mice, this marrow appears to be more resistant to inflammation and other hallmarks of ageing. “By having this expanding skull bone-marrow compartment that remains healthy and functional, we think that’s playing a very critical role in trying to suppress or counteract the neuroinflammation that’s happening during ageing.”
Nature Podcast | 35 min listen
Subscribe to the Nature Podcast on Apple Podcasts, Spotify or YouTube Music, or use the RSS feed.
This post was originally published on here







