Politics
Canada and the United States are about as closely allied and economically integrated as any two countries can be, but that doesn’t mean everything’s always “A-Ok, Eh.” Here are some of the biggest sticking points historically and today in relations between these two North American giants.
24/7 Wall St. Insights
- After the major expansion-era border disputes were settled, relations between the U.S. and Canada began to improve.
- Some of the main areas of disagreement between the two countries today have to do with maritime borders, trade tariffs, and energy policy.
- Also: 2 Dividend Legends To Hold Forever
Colonial History

The American colonies had been settled by Britain for over 150 years before what is today eastern Canada was wrested from the French and added to the empire in 1763. Only about 90,000 people lived there compared to about 1 million in the 13 American colonies. Canadians were invited to join the Revolution in 1776, but having just lost a war to the British a decade earlier, decided to pass on a rematch.
American Invasions

The American military invaded Canada during the Revolution and during the War of 1812 but were unable to rouse the Canadians to revolution nor hold 0n to their territory. Tens of thousands of loyalists fled the American colonies to Canada, particularly to New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, during the Revolution. Their influence contributed to a certain degree of anti-Americanism in Canada.
The Civil War

The British provided some assistance to the Confederacy during the American Civil War by helping them develop a navy to get past the Union naval blockade. Some American politicians demanded that the British pay $2 billion in reparations or cede all of Canada. After arbitration, the British agreed to apologize and pay $15.5 million in damages.
The Washington Border
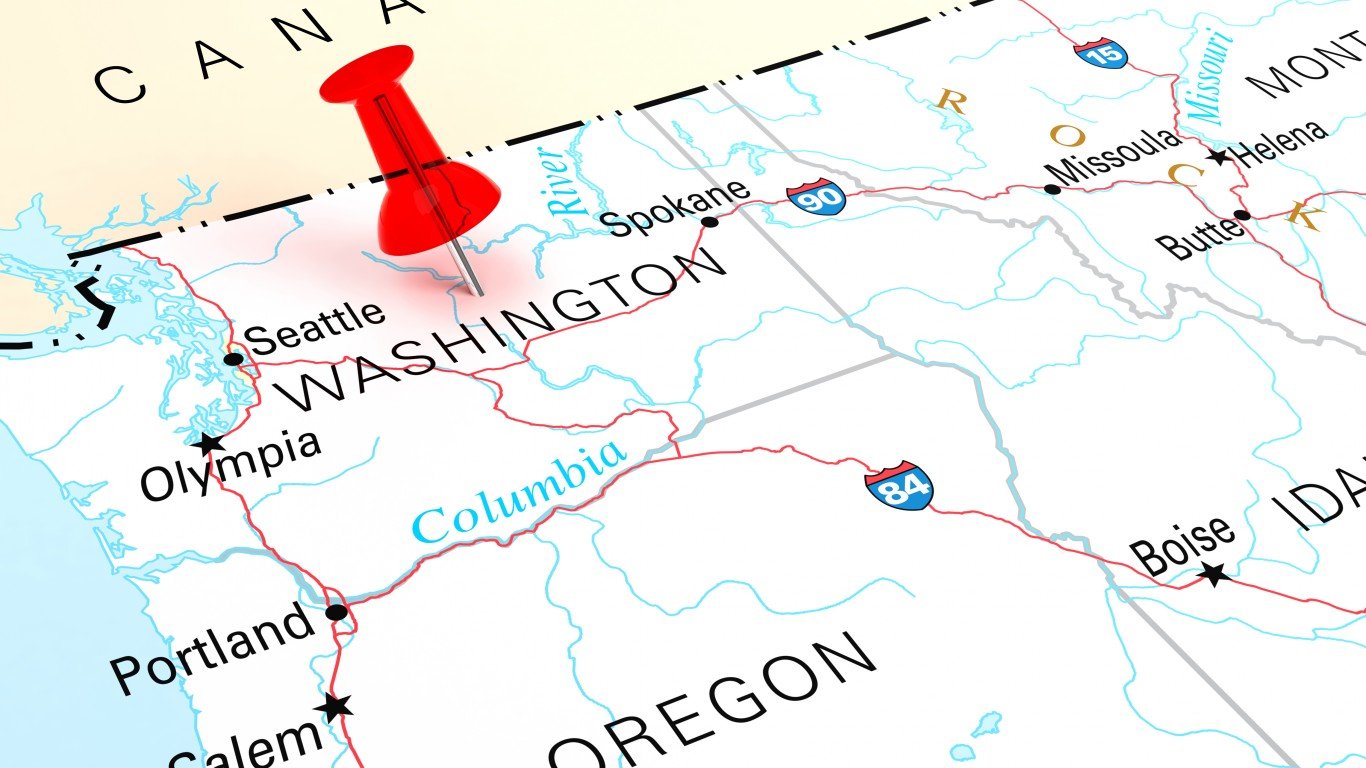
In the 1840s President Polk agreed to split the Oregon Country peacefully with the British, though he had threatened to go to war to claim all of British Columbia for the U.S. But by reaching this settlement, he could instigate the Mexican War and seize the bigger prizes of California and other areas to the southwest without having to fight the British at the same time.
The Alaskan Panhandle
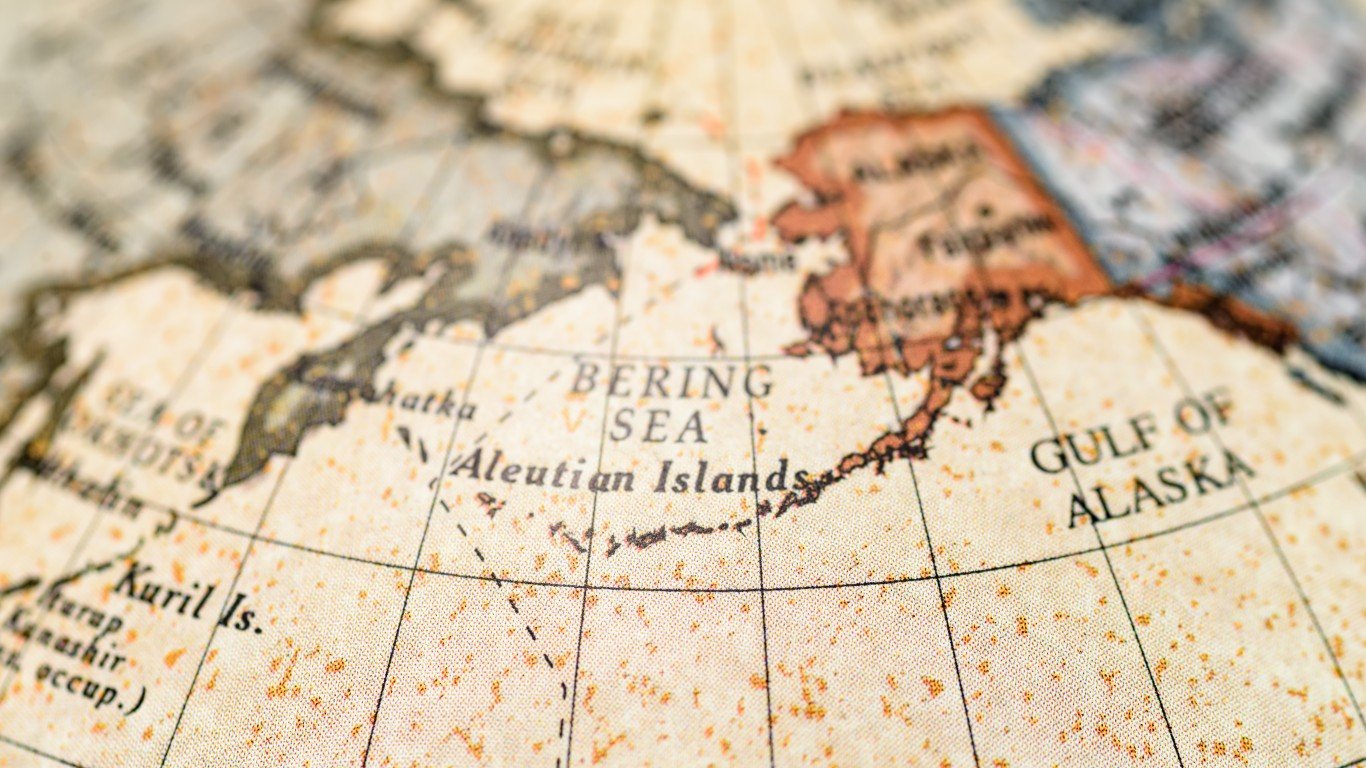
After the U.S. purchased Alaska from Russia in 1867, Canada wanted the Alaskan panhandle or at least enough of it to provide a convenient Pacific port for the Yukon territory, where gold was discovered. This would be a faster, cheaper, and safer route to exporting the region’s gold and bringing in miners and supplies, rather than having to go overland through the dangerous and untamed Canadian Rockies. Wanting to improve relations with the United States, Britain did not press Canada’s claim and the U.S. was able to retain the whole panhandle. This caused a lot of resentment against Britain in Western Canada and contributed to Canadian nationalism.
Atlantic Territorial Disputes
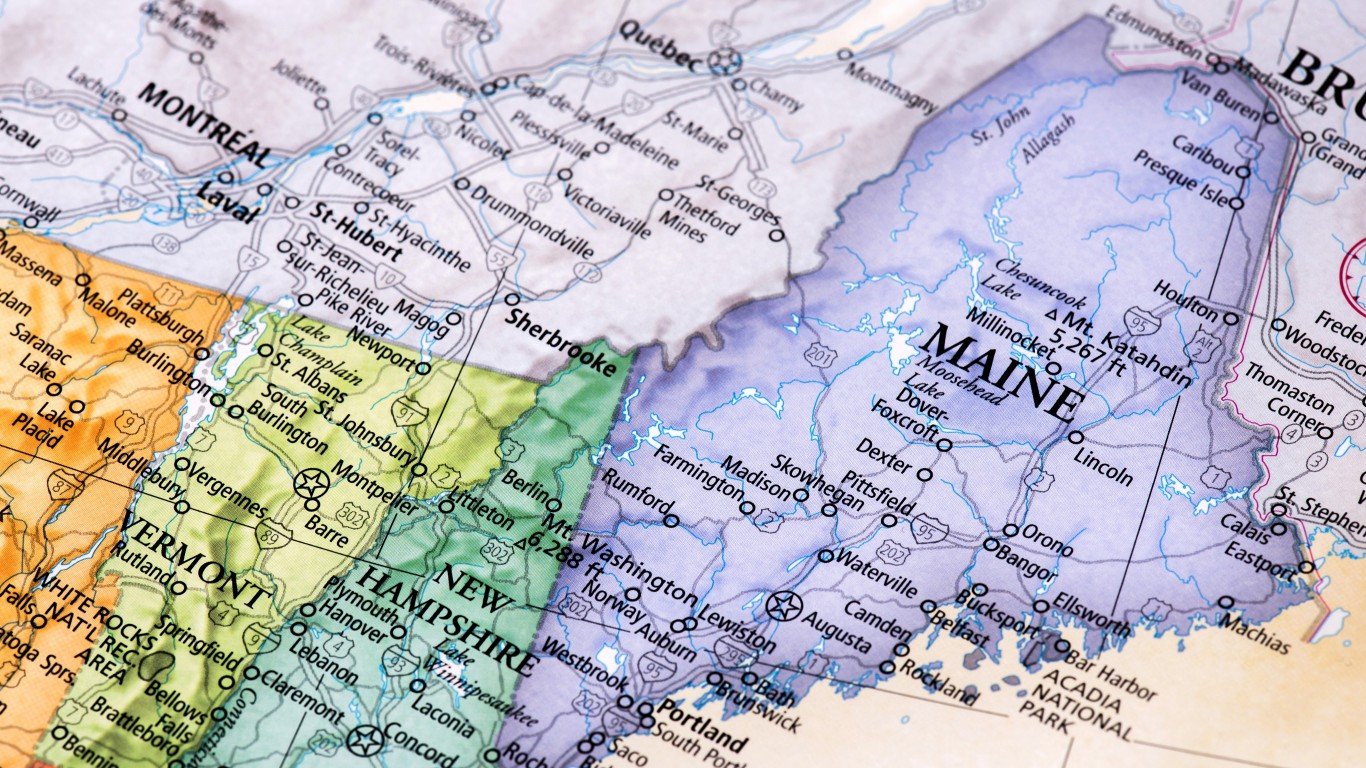
Seal Island and North Rock Island are disputed between Maine and New Brunswick. These islands are small but important because the surrounding area of the ocean is one of the best lobster fishing grounds in the world.
Pacific Territorial Disputes
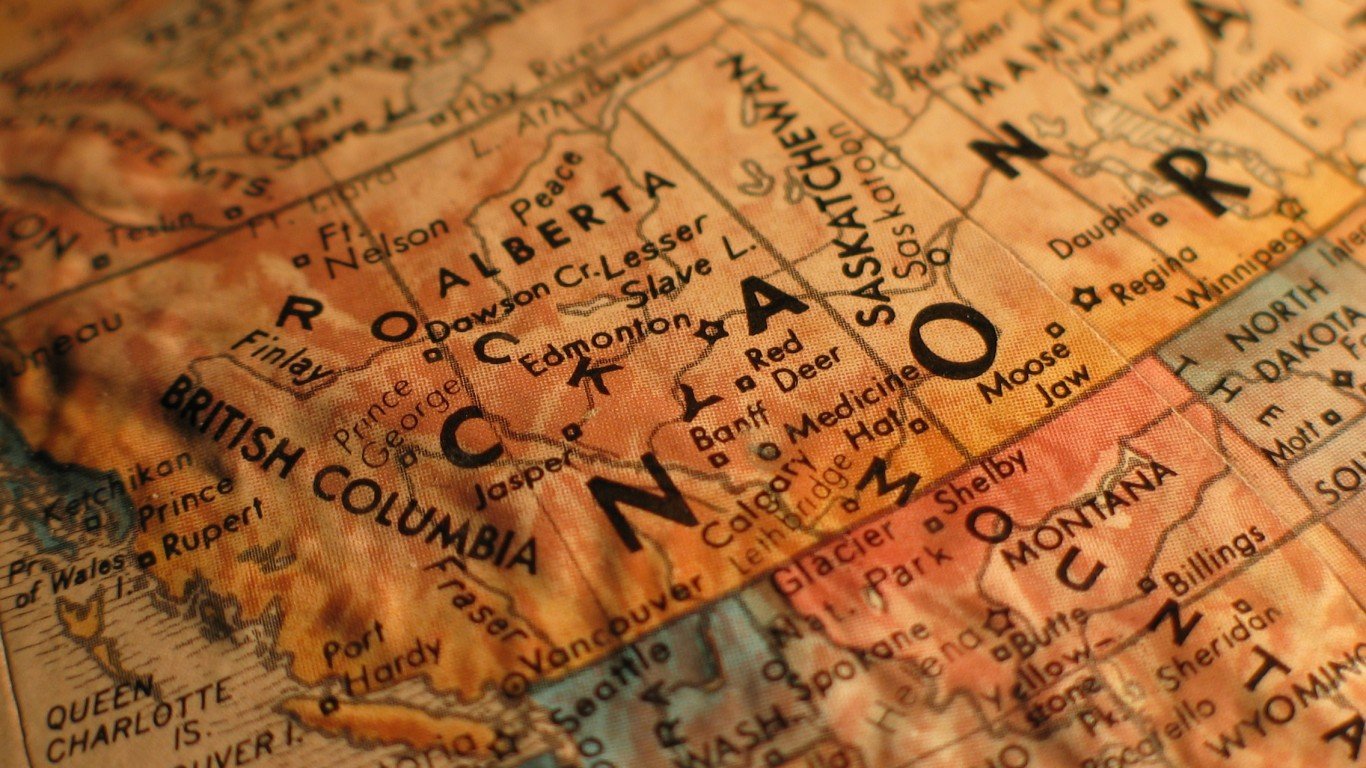
- The boundary between Washington State and British Columbia in the Pacific Ocean after the mouth of the Strait of Juan de Fuca is in dispute.
- Alaska and British Columbia have conflicting claims to the Dixon Entrance at the southern end of the Alaska panhandle.
Arctic Territorial Disputes

- The maritime boundary between Alaska and the Yukon Territory has not been settled. This area might have oil or other significant resources.
- The United States and other countries consider the Northwest Passage between Canada’s northern islands to be international waters but Canada considers this area part of its internal waters. This is important because climate change might make this into a major sea trade route between Europe and Asia.
Softwood Lumber

Canada, the United States, and Mexico have a free trade agreement but there are still disputes over specific commodities. The U.S. taxes Canadian lumber because it says that Canada subsidizes its lumber industry and creates unfair competition with American producers.
Dairy Products

Canada uses a supply management system to regulate dairy imports, so that after a certain quota has been reached, imported milk is taxed 240% and butter 300%. The United States objects to this system as a form of trade protectionism and out of step with practices in other industrialized countries.
American Media

Canada is flooded with American media and wants to protect its culture from Americanization. It has done things like subsidizing Canadian media companies and requiring a certain percentage of Canadian-made content to be broadcast and distributed. The United States wants an end to these practices, which they say creates unfair competition that hurts American media companies.
Oil Exports

As of 2010, almost 100% of Canadian petroleum products were exported to the United States. However, that ready market source for them is endangered by two developments:
- The U.S. developed fracking technology that released huge domestic supplies of petroleum products and reduced the demand for foreign imports.
- Heightened concern for climate change and the movement toward more sustainable energy sources is forecast to reduce the demand for carbon fuels in North America and Europe.
The Keystone Pipeline

The Keystone Pipeline transports oil from Alberta to a junction point in Nebraska, from which it goes on to refineries in Illinois and Oklahoma. There were plans to build a new Keystone XL pipeline in a more direct line from Canada to Nebraska and on to the Texas coast for export. This had to be cancelled due to fierce opposition from American environmentalists.
The India-Canada Dispute

Canada is currently involved in a serious diplomatic dispute with India. Canada says India was behind the assassination of a Canadian Sikh citizen who advocated creation of an independent Sikh country called Khalistan to be carved from Indian territory. The two countries have been expelling each other’s diplomats and have frozen discussion of two pending trade agreements. Both Canada and India are highly important countries to the United States so this breakdown in relations between them is bad for U.S. interests. Rather than choose between them, the U.S. would like to play both sides.
However, U.S. State Department spokesperson Matthew Miller recently said in a press conference that the United States was disappointed India was not making a more serious effort to cooperate in the investigation and resolve the dispute. This would seem to indicate that, given the choice, the U.S. would pick Canada in this situation. But it also indicates that the United States may have run out of patience that back-channel efforts had not led to a resolution and decided that public pressure on India might get better results. The outcome remains to be seen, but there is no doubt Canada appreciates this public show of American support.
Essential Tips for Investing (Sponsored)
A financial advisor can help you understand the advantages and disadvantages of investment properties. Finding a qualified financial advisor doesn’t have to be hard. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three financial advisors who serve your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If you’re ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
Investing in real estate can diversify your portfolio. But expanding your horizons may add additional costs. If you’re an investor looking to minimize expenses, consider checking out online brokerages. They often offer low investment fees, helping you maximize your profit.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.
This post was originally published on here







