This post was originally published on here
Climate change is increasing the likelihood of massive hurricanes and typhoons in the western Pacific, North Atlantic, and Gulf regions.
New research shows that the ocean conditions responsible for the most powerful hurricanes and typhoons are becoming warmer in both the North Atlantic and the Western Pacific. These changes are driven by heat stored in warm ocean water that reaches far below the surface. Scientists estimate that human-driven climate change may account for as much as 70% of the increase in these storm-forming hot spots.
As these hot spots grow, they raise the chances that extremely intense tropical cyclones, including potential Category ‘6’ storms, could make landfall in densely populated regions.
“The hot spot regions have expanded,” said I-I Lin, a chair professor in the Department of Atmospheric Science at the National Taiwan University.
Lin recently presented the research during an oral session on tropical cyclones at AGU’s 2025 Annual Meeting in New Orleans, Louisiana, on Wednesday, 17 December.
Rethinking the Upper Limits of Storm Strength
Lin has been interested in the strongest hurricanes and typhoons for more than a decade. Typhoon Haiyan—also known as Super Typhoon Yolanda—struck the Philippines at maximum intensity in November 2013, killing thousands of people. The next year, Lin and her colleagues published a paper calling for the need for creating a new category of tropical cyclones—6—for the very strongest storms like Haiyan, in the AGU journal Geophysical Research Letters.
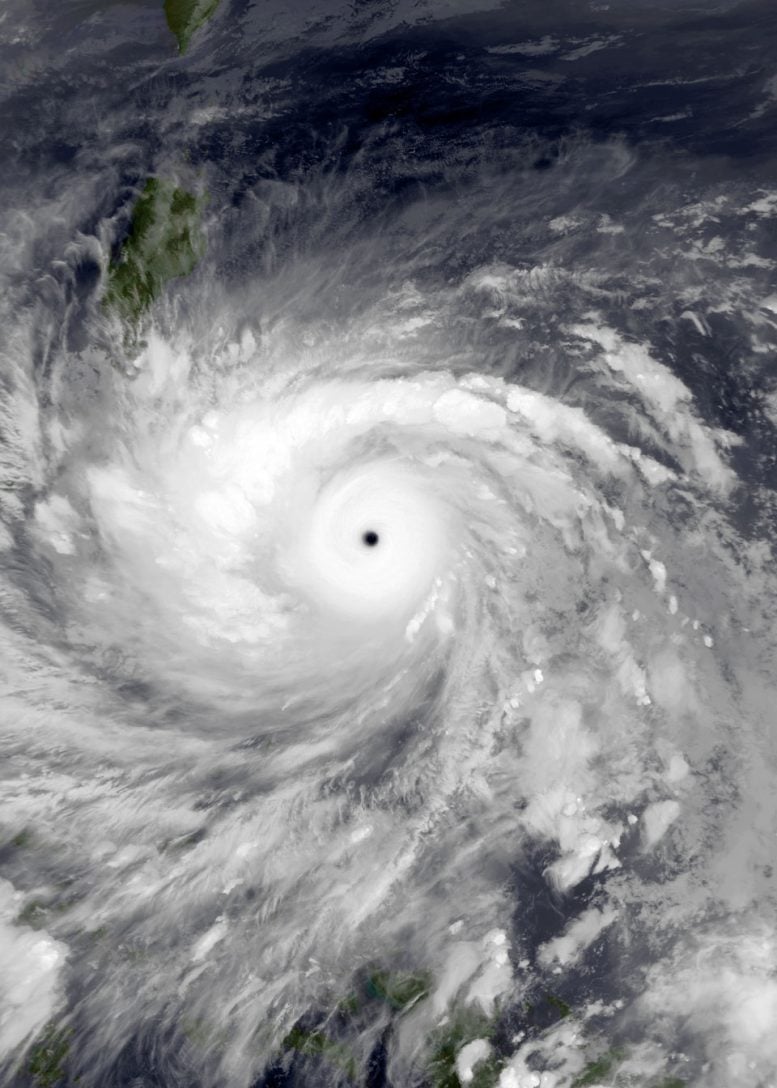
Category 6 tropical cyclones would include those that exceed a wind intensity of 160 knots, Lin and her colleagues argue. Previously, any storm with winds above 137 knots were considered Category 5—most official weather agencies still recognize Category 5 tropical cyclones as the strongest. But since most other categories include a window of about 20 knots, Lin said it makes sense to create a Category 6. Category 4, for example, includes storms with wind intensity of 114-137 knots.
Some of the best-known of these storms include Hurricane Wilma in 2005, the most intense hurricane recorded in the Atlantic basin, Typhoon Haiyan and Typhoon Hagibis, which struck Tokyo in 2019. The latter was among the costliest in terms of destruction from rain and wind, Lin said, even though it had downgraded in intensity by the time it hit the Japanese capital. Finally, Hurricane Patricia, which formed in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of Mexico, was the strongest tropical cyclone ever recorded, with wind intensity of up to 185 knots—enough to make it considered a Category 7 storm, if such a thing existed, Lin said. “Patricia was the king of the world,” she added.
Burgeoning ocean hotspots feed big storms
Lin and her colleagues looked back at all large storms recorded in the past four decades or so, and found that these Category ‘6’ storms are increasingly common. In three decades from 1982 to 2011, there were eight tropical cyclones that had wind intensity of more than 160 knots. In the more recent decade she examined, from 2013 to 2023, there were 10 Category 6 tropical cyclones. So, of 18 Category ‘6’ cyclones that occurred the past 40 years or so, 10 of them happened in the last decade.
Lin’s ongoing recent work, the topic of her discussion at the American Geophysical Union’s 2025 Annual Meeting, reveals that most of these Category ‘6’ tropical cyclones occur in hot spots. The largest hot spot for these massive storms is in the Western Pacific east of the Philippines and Borneo, while another hot spot lies in the North Atlantic around and to the east of Cuba, Hispaniola and Florida.
Their work also reveals that these hot spots are growing in size—the North Atlantic hot spot has expanded eastwards past the northern coast of South America and westwards into much of the Gulf, while the Western Pacific has grown as well.
Why Deep Warm Water Matters
The conditions that drive Category ‘6’ storms are driven by warmer subsurface water as well as warm surface water. In other regions, big storms often churn up the ocean. As cool water is drawn into the surface, it can cool the storm itself, reducing its intensity. But since warm water is so deep in these hot spot regions, the cyclones don’t have a chance to cool as much. Just the same, Lin cautions that not every storm that arises in these hot spots will become a Category ‘6’ tropical cyclone—the atmospheric conditions have to be right as well. “The hot spots are a necessary but not sufficient condition,” she said.
Analysis of the factors driving this expansion of deeper warm water in these hot spots has revealed that global warming and natural variability in temperature both play a role. But overall, the team estimates that human-caused climate change is responsible for about 60-70% of the increased size in these hot spots—and consequently, of Category ‘6’ tropical cyclones.
Lin said that recognition of Category ‘6’ tropical cyclones by weather agencies could help cities plan more appropriately for the impact of coming storms—especially in hot spot areas where they are becoming more common. “We really think there is a need just to provide the public with more important information,” Lin said.
Meeting: AGU’s Annual Meeting
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
Follow us on Google and Google News.





