This post was originally published on here
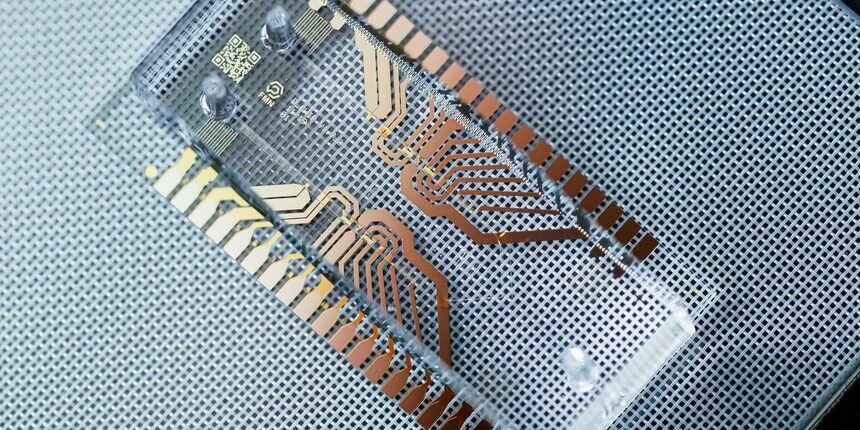
Microfluidics is all about controlling fluids in channels thinner than a human hair, which makes it practical for accelerating scientific discovery. This miniaturized control helps unlock breakthroughs in drug development, disease diagnostics, environmental testing, and chemical synthesis. It’s like fitting an entire lab onto a chip, opening the door to more efficient science that moves innovation forward in ways traditional methods can’t match.
What is microfluidics and how does it work?
Microfluidics guides the flow of tiny volumes of liquid through microchannels using compact systems of microchips, pumps, valves, and sensors. At this small scale, surface effects and fluid viscosity take over 1, making laminar flows more stable and predictable than turbulent flows in larger systems.
This controlled environment allows for faster chemical or biological reactions, minimal sample consumption, lower operational costs, and extremely high precision. To build these systems, scientists use advanced fabrication techniques like soft lithography, 3D printing, and photolithography. These methods enable the creation of custom designs tailored to specific experiments. The blend of fine control and modern engineering makes microfluidics influential in scientific research.
Genomics and DNA analysis
Microfluidics transforms the field of genomics with miniaturized tools that make gene sequencing and polymerase chain reaction amplification faster and incredibly efficient. Managing fluids at the microscale reduces the amount of reagents and time required for large-scale genomic studies, which cuts down on costs and complexity.
This innovation is especially valuable in fast-moving fields like forensics, where trace amounts of DNA can provide vital evidence. It benefits ancestry tracing with high-throughput analysis to reveal deep genetic connections. It also has a growing role in epidemiology by helping scientists quickly track disease patterns and mutations. With microfluidics, genetic research speeds up and becomes more scalable and accessible.
Drug development and personalized medicine
Pharmaceutical companies increasingly turn to microfluidics for high-throughput screening. This technology allows them to test drug compounds quickly and efficiently using minimal materials, speeding up the discovery process while delivering reliable, high-resolution data. Microfluidizers are a key part of this setup because they precisely control particle size 2. They are essential where components must be small enough to trigger the right immune response.
Beyond screening and formulation, microfluidics powers organ-on-chip technology, which mimics human organ behavior more accurately than traditional petri dish models. These help predict how real patients might respond to specific treatments, reducing the need for animal testing and speeding up clinical validation.
Environmental monitoring
Microfluidics offers compact tools that can accurately detect contaminants in water or air. These systems analyze tiny fluid samples in real time, making it possible to spot pollutants, heavy metals, or pathogens on-site. Speed and portability are pivotal for regulatory bodies that need quick answers during contamination events or routine safety checks.
Climate scientists also rely on these platforms to gather precise data on environmental shifts, which helps them monitor pollution trends and support more sustainable decision-making. With microfluidics, protecting natural resources becomes more proactive and data-driven.
Medical diagnostics and point-of-care testing
Microfluidic chips enable fast, low-cost tests using just a small drop of blood or saliva. These compact devices precisely handle fluid samples, which allows the real-time detection of glucose levels and cancer biomarkers without a traditional lab. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these platforms were influential in rapid testing efforts, offering accurate results at scale and speed.
Beyond diagnostics, these chips are also used in nanoparticle preparation 3, cell analysis, and small-scale cell culture, which makes them versatile tools for research and clinical applications. Their portability and efficiency are especially valuable in remote or low-resource settings, where access to full-scale laboratory infrastructure is limited but timely results are critical for patient care.
Cell biology and single-cell analysis
Microfluidics allows researchers to isolate and study individual cells with exceptional precision. Because these structures are similar in size to a single cell [4], they can easily trap, move, and analyze cells using only tiny amounts of reagents and samples. This control helps scientists observe how cells behave, offering valuable insight into immune responses and cellular development.
It’s particularly impactful in cancer research, tracking the behavior of individual tumor cells to find more targeted therapies. Likewise, in stem cell therapy, it assists by monitoring cell differentiation, which is crucial for successful treatments. With microfluidics, the complex world of cell biology becomes more customizable, paving the way for breakthroughs in research and medicine.
Chemical synthesis and reaction engineering
Microfluidics lets scientists fine-tune reaction conditions with remarkable precision. This approach leads to more consistent results and fewer unwanted byproducts, making experiments more reliable and repeatable. In particular, these platforms support continuous-flow chemistry so reactions happen in a steady stream rather than batch by batch.
This is especially beneficial in materials science and nanotechnology labs, where professionals produce high-quality particles or compounds that often depend on maintaining exact conditions. By streamlining complex processes and reducing the risk of error, microfluidics helps researchers create next-generation materials faster and more safely.
What’s next for microfluidics?
Exciting integrations with AI and the IoT shape the future of microfluidics, paving the way for smart lab systems that can automate, analyze, and optimize experiments in real time. At the same time, advances in 3D printing improve how these devices are made. They allow researchers to produce intricate microchannels and structures [5] with high precision and unmatched flexibility rapidly. This speeds up prototyping and opens up more creative design possibilities.
These innovations also drive microfluidics into wearable technology. For example, real-time health monitoring becomes possible through compact, skin-friendly devices that track hydration, glucose or stress levels on the go. As these tools become smaller, smarter, and more affordable, they have the potential to democratize science. They put powerful diagnostic and research capabilities into the hands of more people, not just those in elite labs.
The future flows through microfluidics
Microfluidics delivers speed, accuracy, and scalability across a wide range of scientific fields by controlling fluids at the microscopic level. It’s breaking traditional lab boundaries by shrinking complex experiments onto chips, which makes research faster and more efficient. As scientists explore what microfluidics is capable of, it shapes future innovations in health care, environmental science, agriculture, and beyond.
Notes
1 Introduction to Microfluidics and Its Applications at ElveFlow.
2 Microfluidizers for Vaccine Development at New Life Scientific.
3 What Is Microfluidics at News Medical Life Sciences.
4 Microfluidic Biochips for Single-Cell Isolation and Single-Cell Analysis of Multiomics and Exosomes at National Library of Medicine.
5 Next-Generation Microfluidics for Biomedical Research and Healthcare Applications at ResearchGate.