This post was originally published on here
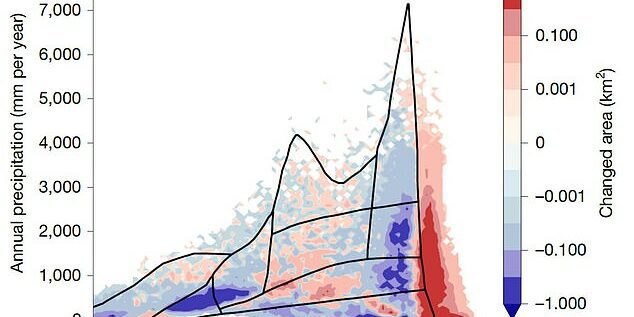
The Amazon rainforest is shifting into a ‘hypertropical state’ that has not been seen for tens of millions of years, scientists have warned.
This new, hotter climate could be commonplace by 2100, and will see the rainforest experience more frequent and intense droughts.
Worryingly, experts from the University of California, Berkeley, say this could lead to widespread tree die–off.
In turn, this will impair Earth’s ability to remove carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, since tropical rainforests absorb more carbon emissions than any other biome.
The only way to prevent the hypertropical state from occurring is to curb greenhouse gas emissions, according to Jeff Chambers, lead author of the study.
‘It all depends on what we do,’ he said.
‘It’s up to us to what extent we’re actually going to create this hypertropical climate.
‘If we’re just going to emit greenhouse gasses as much as we want, without any control, then we’re going to create this hypertropical climate sooner.’
Usually, the dry season in the Amazon lasts from July to September and brings hotter–than–normal conditions.
However, in hypertropical conditions, the dry season is extended – putting more stress on trees.
‘When these hot droughts occur, that’s the climate that we associate with a hypertropical forest, because it’s beyond the boundary of what we consider to be tropical forest now,’ explained Professor Chambers.
Worryingly, the study found that by 2100, hot drought conditions could occur as many as 150 days each year.
In turn, this could increase tree mortality by 0.55 per cent.
‘We showed that the fast–growing, low wood–density trees were more vulnerable, dying in greater numbers than high wood–density trees,’ Professor Chambers said.
‘That implies that secondary forests might be more vulnerable to drought–induced mortality, because secondary forests have a larger fraction of these types of trees.’
Since the annual tree mortality is slightly more than one per cent, an extra 0.55 per cent may not seem like much.

However, Professor Chambers explained that it has a cumulative impact on the forest – meaning over time, it could be catastrophic.
What’s more, the researchers say that hypertropical conditions are also likely to appear outside the Amazon in rainforests in western Africa and across Southeast Asia.
As global temperatures continue to rise, extreme droughts will increasingly occur throughout the entire year, the researchers added.
‘Present–day hot droughts are harbingers of this emerging climate, providing windows of opportunity to better understand tropical forest responses to increasingly extreme future conditions,’ the authors wrote.